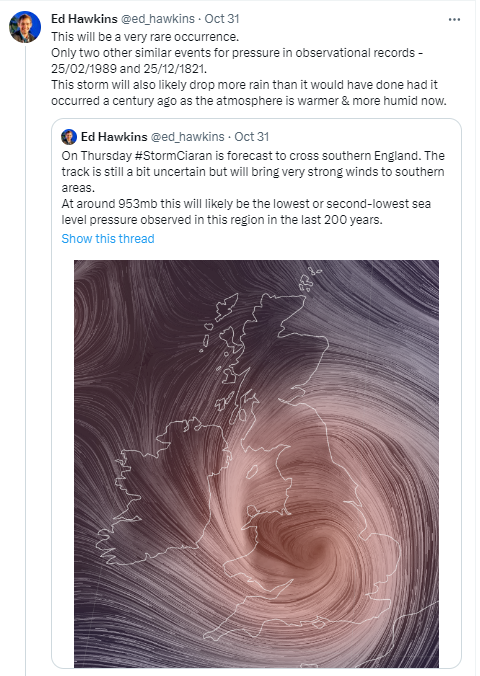
The lowest pressure recorded in the southern UK happened on February 25th 1989 when the barometer fell to 942.4mb.
I was also reminded this week of another occurrence of extraordinary low pressure in southern England on Christmas Day 1821. Luke Howard’s Climate of London recalls the event in his December summary where, he states, the air pressure fell to 27.83 inches (942.4mb).
This month is remarkable for a depression of the barometer which for London at least or its vicinity is nearly without a precedent on record. The lowest observation here given 27.83 in was obtained at Tottenham from a portable barometer of Sir H Englefield’s construction about 5am on the 25th.
Luke Howard
In what appears to be remarkably similar to what is unfolding with Storm Ciaran Howard added that despite the low pressure the weather on Christmas Day was ‘very fine’, a day that was sandwiched by much rainy weather.
In his entry Howard explains:
We had no storm of wind of any consequence after this great depression which it should be remarked had been coming on for about two weeks. It appears by the papers that a like state of the barometer was extensively observed at the same time on the continent and that very tempestuous weather attended it far to the south of our island.
Luke Howard
Howard also received a letter from Thomas Squire of Epping who wrote.
The fall of the barometer has been as wonderful as the fall of rain. On the 24th at midnight my barometer was 27.76 in. It continued nearly stationary till about six next morning when it was 27.73 in. This was its minimum altitude shortly after it began to rise at 8am.
Thomas Squire
Squire’s readings, taken at Epping (105m), can be adjusted for sea level and compared with the hourly trace for Storm Ciaran. Taking this into account the barometer actually bottomed out at 927.6mb! Plotted against Storm Ciaran the behaviours of the two depressions are remarkably similar.
Howard would go on to discuss his findings with the Royal Society the following month in January. He remarks that the low pressure was notable in that it happened in the same year that notably high pressure was recorded in the February. Just like this year! I recorded 1060.1mb on February 5th.
Though low by southern UK standards there have been many deeper depressions to the north.







































You must be logged in to post a comment.